Frequency of IKZF1 Deletions in a Peruvian Population with B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Background: B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL) is an aggressive disease with worse outcomes in older patients, and latino ethnicity. Additionally, Latino populations are at higher risk of developing B-ALL.IKZF1is an essential lymphoid transcription factor with deletions (ΔIKZF1)implicated in treatment failure and relapses. We aimed to evaluate the frequency ofIKZF1deletions in a cohort of Peruvian patients with newly diagnosed B-ALL.
Methods: We collected diagnostic bone marrow samples from 41 consecutive patients with B-ALL diagnosed between 2015-2019 at Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplasicas (INEN; Lima, Peru). Bone marrow samples were cryopreserved prior to induction treatment. DNA was extracted using High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit (Roche) at INEN. Samples with adequate DNA were screened forΔIKZF1by multiplex endpoint PCR covering four main deletions - dominant negative Δ4-7 or the loss of function Δ2-7, Δ4-8, and Δ2-8 IKZF1 deletions at UCL Cancer Insitute (London, UK) using the primers described by Caye et. al. We analyzed outcomes byIKZF1status.
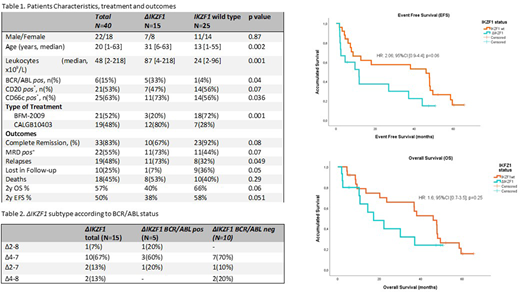
Results: Forty-one cases were enrolled during the study period. Clinical characteristics are presented in Table 1. Median age was 20 years[1-63]. Fifteen∆IKZF1cases (37%) were detected (67%BCR-ABL1 negand 33%BCR-ABL1pos).Cases withΔIKZF1were older than those with wild-typeIKZF1(median age 31 vs 13 years, p=0.002). Median presenting white blood count (WBC) was 48 x109/L [R:2-218], with a higher WBC inΔIKZF1compared to wild-type (87 vs 24 x109/L, p=0.001). The most frequent deletion was ∆4-7 (sevenBCR-ABL1 negand threeBCR-ABL1 pos) additional deletions are described in table 2. All patients received intensive 'pediatric-based' treatment, 21 with BFM-2009 and 19 with the CALGB 10403 protocol. CR rates after induction were 67% and 92% for∆IKZF1and wild-type cases, respectively. Eleven (73%) of patients with∆IKZF1subjects (73%) were MRD positive by flow cytometry after induction compared to 11 (44%) among wild-type. At a median follow-up of 2 years EFS was 38% in the∆IKZF1group and 58% in the wild type group, correspond OS was 38% and 58%, respectively.
Conclusion: A high frequency of IKZF1 deletions was found in a Peruvian population with B-ALL and was associated with older age and higher presenting white blood counts. Prospective studies with larger Latino population are warranted to confirm this finding.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal